Physics Theory : Plane Mirrors
Reflection of light is the phenomenon due to which a light ray traveling from one optical medium to another bounces off its surface with a change of angle.
Regular reflection takes place when a parallel beam of light strikes a smooth polished surface and it is reflected back as a parallel beam of light.
Diffused reflection or irregular reflection takes place when a parallel beam of light strikes a rough surface and it is reflected back in different random directions.
A plane mirror is a smooth polished surface that can turn the rays of light into the same medium.
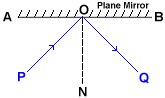
The normal (denoted by line ON in the figure) is drawn at the point of incidence O perpendicular to the plane mirror surface.
The incident ray (denoted by line PO in the figure) corresponds to a ray of light that travels from an optical medium towards the mirror.
The reflected ray (denoted by line OQ in the figure) corresponds to a ray of light that bounces off the mirror surface and travels into the same optical medium in which the incident ray was traveling.
The angle of incidence (denoted by angle PON in the figure) is the angle that the incident ray PO makes with the normal ON.
The angle of reflection (denoted by angle NOQ in the figure) is the angle that the reflected ray OQ makes with the normal ON.
The First Law of Reflection states that the incident ray PO, the reflected ray OQ and the normal ON all lie in the same plane, at the point of incidence.
The Second Law of Reflection states that the angle of incidence PON is always equal to the angle of reflection NOQ.
When a divergent beam of light is incident on a plane mirror, it is reflected back as a divergent beam.
When a convergent beam of light is incident on a plane mirror, it is reflected back as a convergent beam.
When a parallel beam of light is incident on a plane mirror, it is reflected back as a parallel beam.
The following characteristic properties of the image formed by a plane mirror are worth noting :
Lateral inversion occurs when the left side of an object appears as the right side of an image and vice-versa.
|
36 more pages in School Physics Quiz