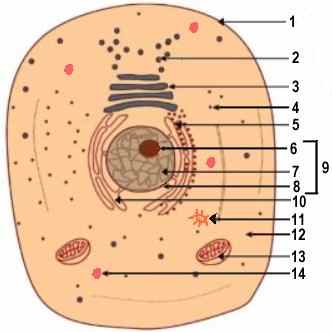
| LABEL (ON DIAGRAM) | CELL PART | EXPLANATION |
| 1 | Cell Membrane | The cell membrane is also known as the plasma membrane. It is the outermost covering of the animal cell. It protects the cell and regulates the entry and exit of substances, namely ions and solutes. |
| 2 | Secretory Granule | The secretory granule is a vesicular structure. It is formed when the substances produced in the endoplasmic reticulum are further processed in the golgi apparatus of the animal cell. |
| 3 | Golgi Apparatus | The golgi apparatus of the animal cell consists of flat vesicular structures placed one on top of the other. It synthesizes and secretes certain substances, namely hormones and enzymes. |
| 4 | Ribosome | The ribosome of the animal cell is chiefly composed of RNA (Ribonucleic Acid). It synthesizes proteins. |
| 5 | Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum | The rough endoplasmic reticulum consists of tubular structures (convulated tubules) lying near the nucleus and has ribosomes attached to it. It provides support to the animal cell.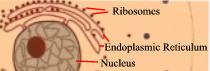 |
| 6 | Nucleolus | The nucleolus is contained in the nucleus of the animal cell, and is round in shape. It synthesizes proteins by producing and storing RNA (Ribonucleic acid). |
| 7 | Nucleoplasm | The nucleoplasm of the animal cell is a dense fluid containing chromatin fibres, which are made up of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid). After cell division takes place, these chromatin fibres undergo certain structural changes, and are called chromosomes. These chromosomes carry the hereditary information of the genes. |
| 8 | Nuclear Membrane | The nuclear membrane is the covering of the nucleus of the animal cell, and has numerous pores. It allows substances to enter and leave. |
| 9 | Nucleus | The nucleus is the most important part of the animal cell, and contains large amounts of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid). It controls and coordinates all the activities and functions of the cell. |
| 10 | Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum | The smooth endoplasmic reticulum consists of tubular structures (convulated tubules) lying near the nucleus and does not have ribosomes attached to it. It provides support to the animal cell. |
| 11 | Centrosome | The centrosome of the animal cell contains one or two centrioles, and is surrounded by microtubules or the centrosphere. It initiates and regulates cell division. |
| 12 | Cytoplasm | The cytoplasm is composed of a mixture of water and soluble organic & inorganic compounds, and contains most of the cell organelles. It is the house of all metabolic functions and activities of the animal cell. |
| 13 | Mitochondrion | The mitochondrion of the animal cell has two layers of membrane, of which the inner one is folded to form cristae. It is the site of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate) synthesis. |
| 14 | Lysosome | The lysosome of the animal cell is a membranous sac budded off from the golgi apparatus, and contains several types of enzymes. It performs intracellular digestion and destroys foreign substances. |