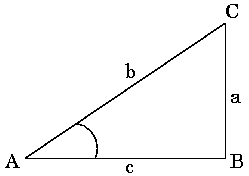|
Contents for Trigonometry Module 1 : Trigonometric Functions
Sin, Cos and Tan Functions
The trigonometric functions of angles are the ratios of the various sides of a triangle. Consider a right-angled triangle ABC as shown in the figure below.
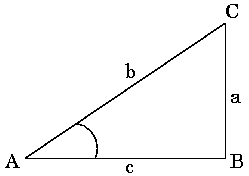
The following terminology is useful.
- Hypotenuse: The side opposite to the right angle in a triangle is called the hypotenuse. Here the side AC is the hypotenuse.
- Opposite Side: The side opposite to the angle in consideration is called the opposite side. So, if we are considering angle A, then the opposite side is CB.
- Base: The third side of the triangle, which is one of the arms of the angle under consideration, is called the base. If A is the angle under consideration, then the side AB is the base.
For angle A (sometimes referred to as angle CAB), the following fundamental trigonometric functions can be defined.
Sine of A = sin A = Opposite Side / Hypotenuse = CB/CA = a/b
|
Cosine of A = cos A = Base / Hypotenuse = AB/CA = c/b
|
Tangent of A = tan A = Opposite Side / Base = CB/AB = a/c
|
|
From the definitions, it can be seen that tan A = sin A / cos A.
Cosec, Sec and Cot Functions
A few more useful functions can be defined.
Cosecant of A = cosec A = 1 / sin A = b/a
|
Secant of A = sec A = 1 / cos A = b/c
|
Cotangent of A = cot A = 1 / tan A = c/a
|
|
From the definitions, it can be seen that cot A = cosec A / sec A
Practice Exercise for Trigonometry Module 1: Trigonometric Functions |
|